Russia’s California Colony
The Russians were among the first Europeans to sense California's potential. Had they not sold their settlement there in 1841, the world could have been a different place.
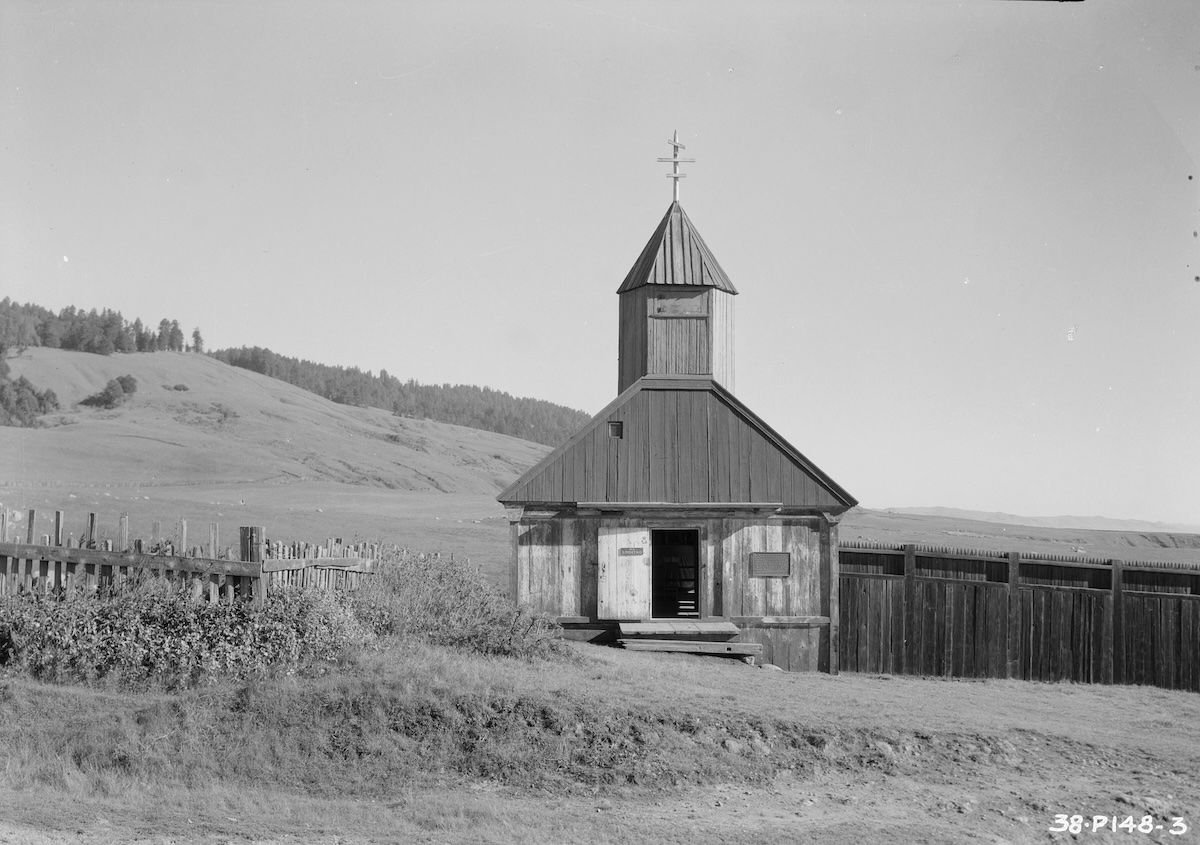

The period of Russian rule in California has almost been forgotten; but, though nothing survives of the little fortress that once commanded a river flowing out into Bodega Bay, they call it Russian river still. In fact, the first Europeans to foresee the possibilities of California were Russians, who came across Siberia, felt their way down the Pacific coast in shitiki—sewn ships of pine logs lashed to boards and caulked with moss—and by the middle of the eighteenth century had started hunting sea otters for their skins in San Francisco Bay. Sometimes they wintered ashore. But these pioneers, the Promyshleniks, were lone venturers. They had no government behind them: Moscow remained unconscious or indifferent.
On the Spanish viceroys in Mexico, however, the rovings of the Promyshleniks had a different impact. True, they were individual adventurers. But such adventurers may found an empire. A Russian California would bar the advance of the Spanish American Empire, and might even push it back to the isthmus of Panama. To forestall the Russians, therefore, Spain moved into California and founded her first colony at San Diego in 1769.